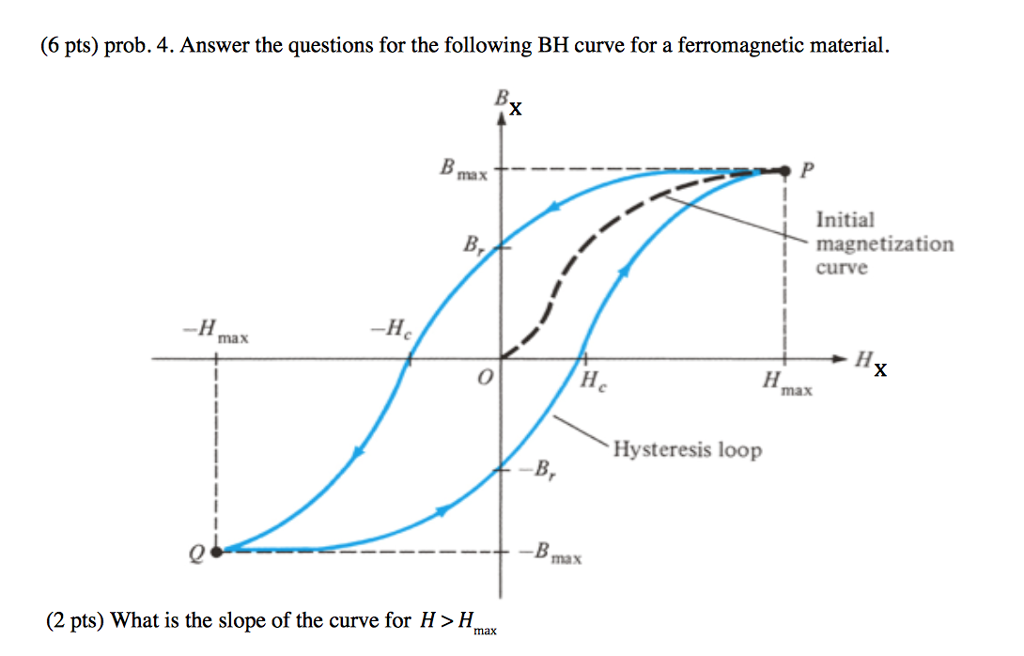
Solved Answer the questions for the following BH curve for a
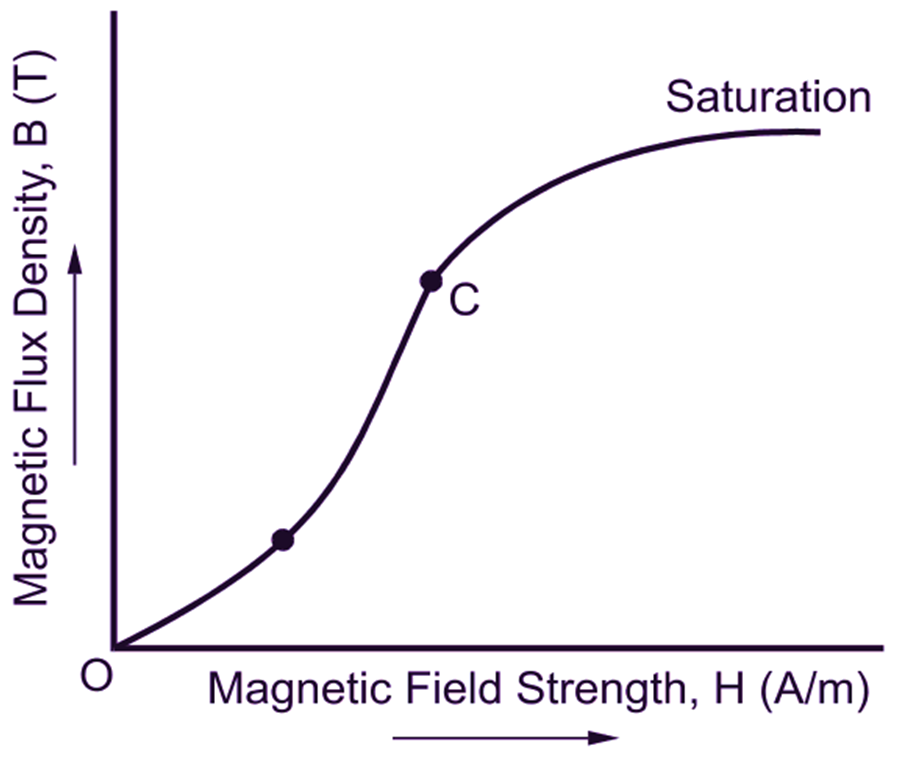
The B-H characteristic is known as the magnetization curve. It shows the behavior of the three regions: the linear region, the knee region, and the saturatio.

Hysteresis Curve Electrical Academia
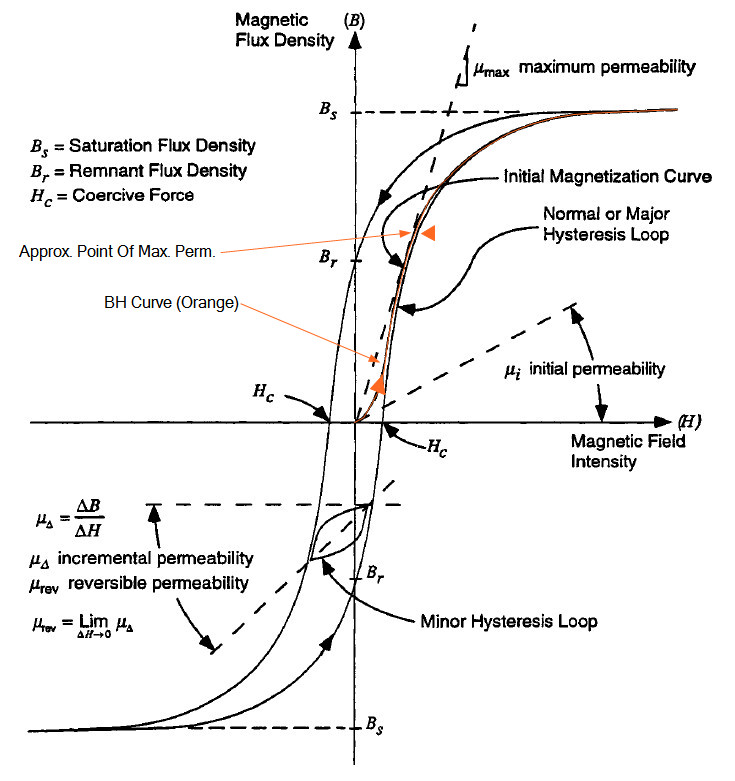
A curve, or loop, plotted on B-H coordinates showing how the magnetization of a ferromagnetic material varies when subjected to a periodically reversing magnetic field, is known as Hysteresis Loop or Magnetization Curve. Non-Magnetic Materials The reluctance of non-magnetic materials is not affected by the density of flux in those materials.

BH curves of the Alnico used. Download Scientific Diagram
Figure 6.2.3 6.2. 3: A hysteresis loop for a polycrystalline specimen of pure iron. The details of the B-H loop are specimen sensitive. The saturation magnetization at room temperature is 2.14 Teslas. The remanent field is B r = 1.22 T, and the coercive field is H c = 79 Amps/m. cubic axes.

BH curve Curve of Materials Hysteresis Curve YouTube
The B-H curve, also known as the magnetization curve, is an integral concept in the study of magnetism and magnetic materials. The 'B' in the B-H curve refers to magnetic flux density, while the 'H' stands for the magnetic field strength. Magnetic Flux Density (B)
BH Curve Curve ElectricalWorkbook
Measuring B-H curves involves expensive equipment and requires considerable skill and experience, and published B-H curves are most often provided only graphically.. There are magnetization models used for modeling hysteresis and/or magnetostriction that can be reduced to just describe magnetic saturation, e.g. using a Langevin function and.
FileBH Curve and Loop.jpg Wikimedia Commons
Hysteresis Loop Definition A curve, or loop, plotted on B-H coordinates showing how the magnetization of a ferromagnetic material varies when subjected to a periodically reversing magnetic field, is known as Hysteresis Loop or Magnetization Curve. The term 'hysteresis' means to lag behind.

Exemplary results of measurement of initial curve (blue... Download Scientific
A BH curve, also known as a demagnetization curve, describes the magnetic qualities of a magnet more completely than a single number like Pull Force or Surface Field. It provides information about the strength of the magnet, how hard it is to demagnetize, and how a magnet's shape (or use in a magnetic circuit) affects matters.

Circuits Inst Tools
Recent development of SPICE, FEM and MoM software often requires the fast and reliable description of BH saturation magnetization curve. In spite of the fact that physical models of BH saturation.
How the BH Curve Affects a Analysis (and How to Improve It) COMSOL Blog
Outline The Definitions of M, B, and H Values on the Magnetization Curves Misconception 1: Coercivity Misconception 2: Induction Does Not Saturate Misconception 3: Symmetry Misconception 4: Scale Final Thoughts References and Further Reading The Definitions of M, B, and H

BH Curve of a typical material Download Scientific Diagram
Figure 1: DC magnetization curve In other words, for same increment in B, one has to apply more excitation in saturation region than in linear region. This is called as DC Magnetization Curve as both Band Hhave same sign. It is interesting to see what hapens when the external magnetic \excitation" is removed or reduced to zero.

curves of nanoparticle formulations loaded with... Download Scientific
By plotting values of flux density, ( B ) against the field strength, ( H ) we can produce a set of curves called Magnetisation Curves, Magnetic Hysteresis Curves or more commonly B-H Curves for each type of core material used as shown below. Magnetisation or B-H Curve
BH Curve problem
Magnetic hysteresis Theoretical model of magnetization m against magnetic field h. Starting at the origin, the upward curve is the initial magnetization curve. The downward curve after saturation, along with the lower return curve, form the main loop. The intercepts hc and mrs are the coercivity and saturation remanence.

Can anyone explain why a BH curve with Hysteresis doesn't result in a highly input
The graph intensity of magnetization (M) vs. magnetizing field (H) gives a closed curve called M-H loop. Consider the portion AB of the curve given below. The intensity of magnetization M does not become zero when the magnetizing field H is reduced to zero. Thus the intensity of magnetization M at every stage lags behind the applied field H.

A. BH Curve Understanding
Saturation is most clearly seen in the magnetization curve (also called BH curve or hysteresis curve) of a substance, as a bending to the right of the curve (see graph at right). As the H field increases, the B field approaches a maximum value asymptotically, the saturation level for the substance.
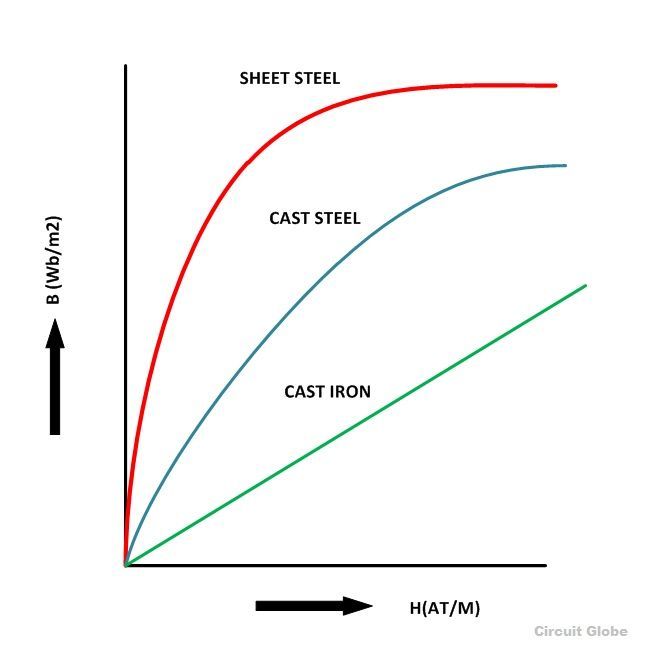
BH Curve Curve ElectricalWorkbook
Thus the B(H) Magnetization Curve is characterized by H, B data columns. The P(B) Core Loss Curve is characterized by a B, P data columns. For each grade, MagWeb contains all these curves in a single 'grade file' in excel format. The magnetization curve plots the magnetic flux density response of the material (B tesla) vs. applied magnetic.
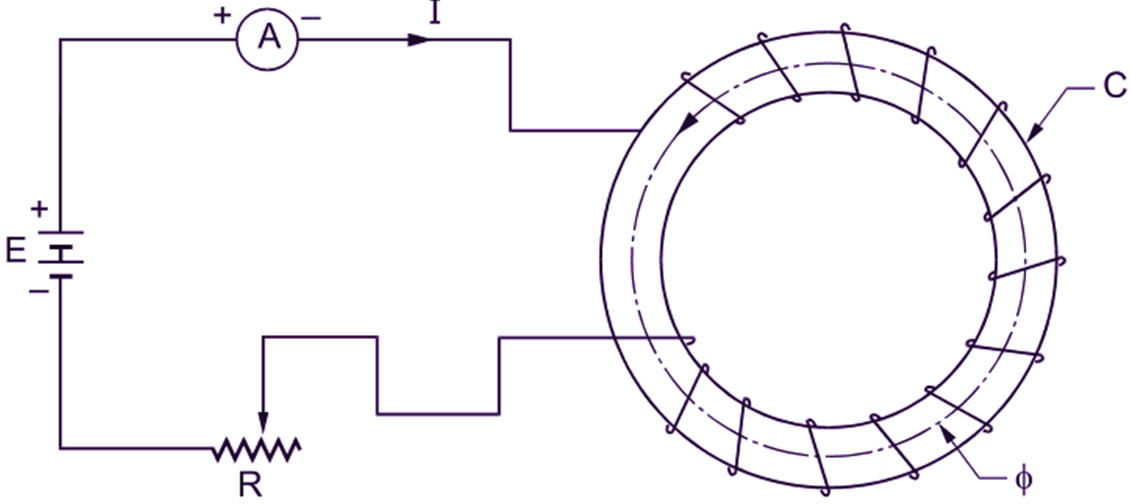
What is Series Circuit? definition and explanation Circuit Globe
The B-H curve or magnetisation curve is the graph plotted between magnetic flux density (B) and magnetising force (H). The B-H curve indicates the manner in which the magnetic flux density varies with the change in magnetising force. The following figure shows the general shape of B-H curve of a magnetic material.